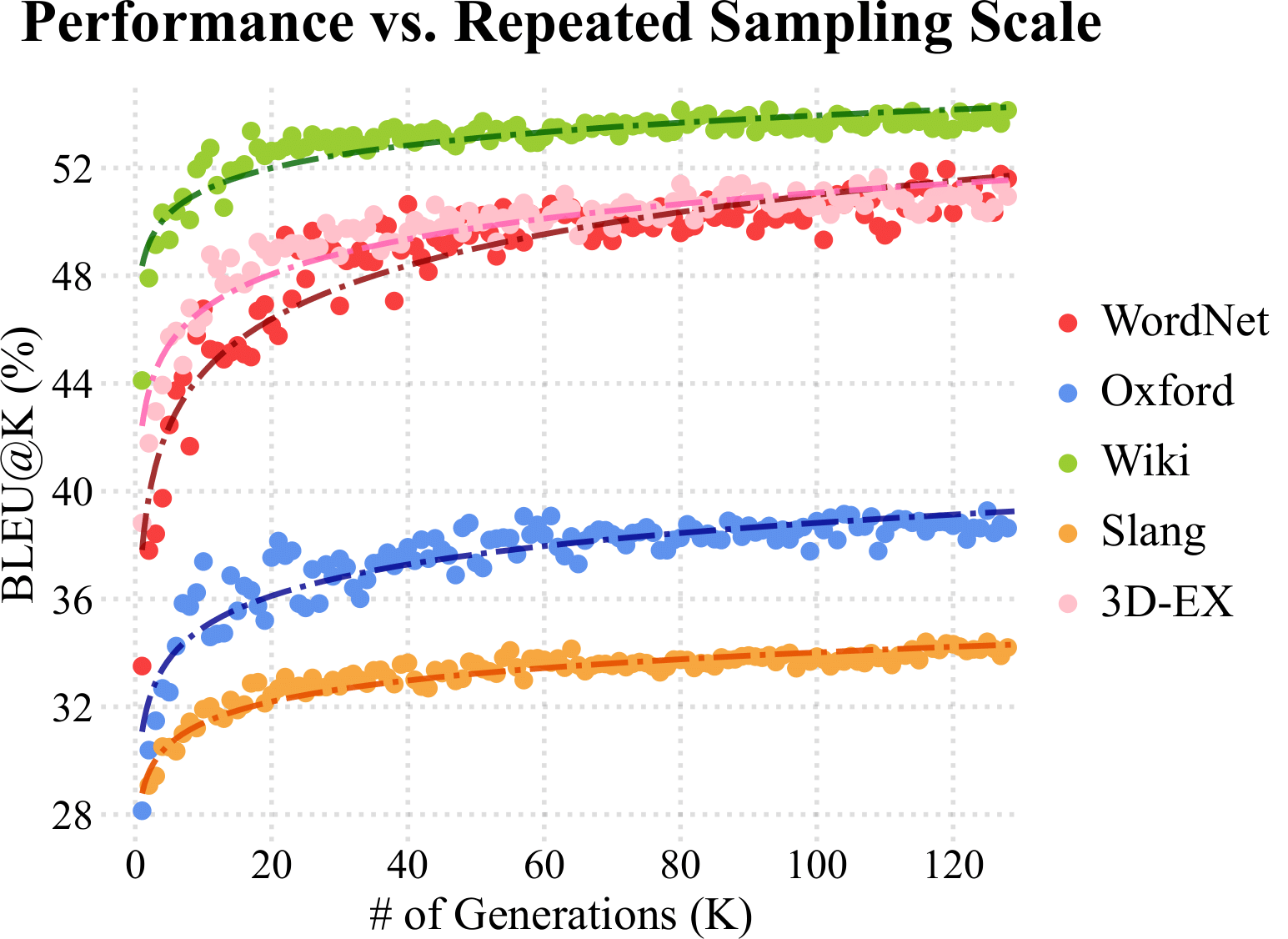
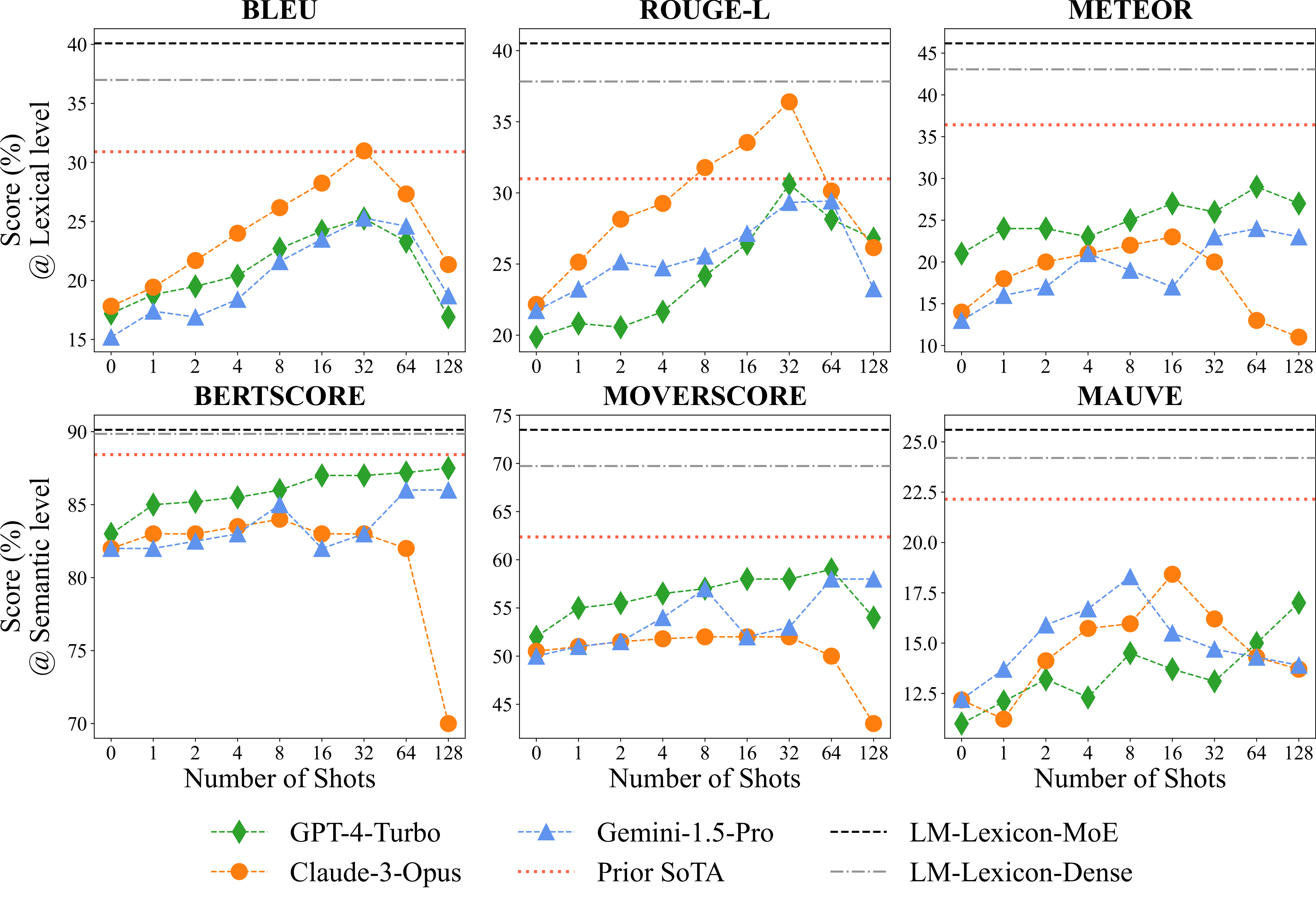
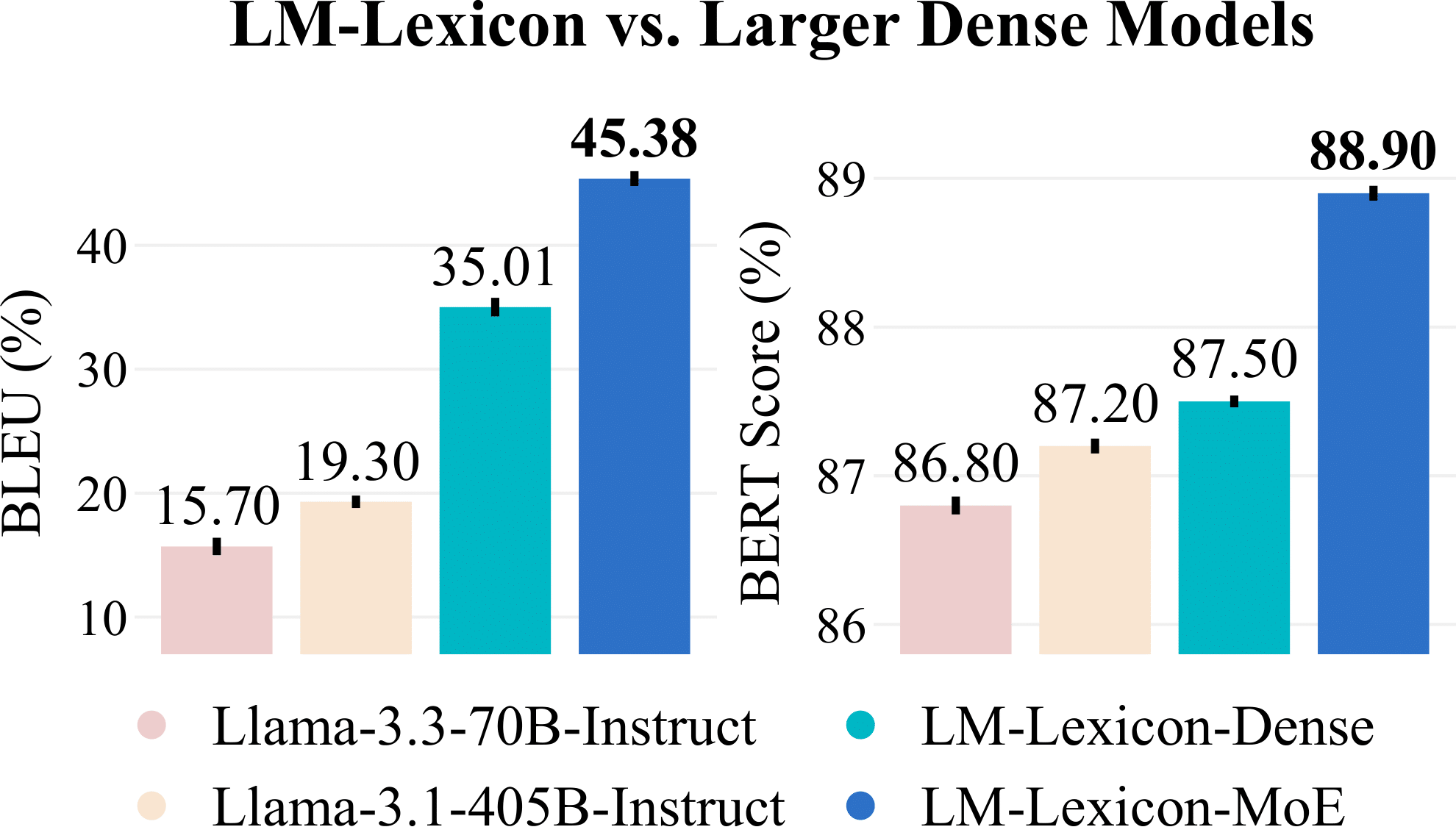
We conduct comprehensive ablation studies to validate the effectiveness of each component in our LM-Lexicon framework. The studies demonstrate significant improvements across multiple dimensions:
Overall Component Analysis
| Training Setup | WordNet | Oxford | Wikipedia | Urban | 3D-EX | Average | Δ from Baseline |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline (Single Model) | 32.14 | 18.92 | 54.23 | 24.67 | 35.81 | 33.15 | - |
| + Random Data Split | 33.47 | 19.84 | 55.12 | 26.13 | 37.05 | 34.32 | +1.17 |
| + Lexical-based Partition | 34.21 | 20.15 | 56.78 | 27.39 | 38.42 | 35.39 | +2.24 |
| + Semantic Clustering | 37.85 | 21.67 | 58.94 | 29.14 | 42.18 | 37.96 | +4.81 |
| + Token-level Routing | 38.72 | 22.11 | 59.43 | 29.87 | 43.55 | 38.74 | +5.59 |
| + Domain-level Routing (Full Model) | 40.09 | 23.35 | 60.31 | 31.26 | 45.69 | 40.14 | +6.99 |
BLEU scores across five benchmarks showing cumulative improvements from each component. Domain-level routing provides the final boost to achieve state-of-the-art performance.
Data Partitioning Strategy Comparison
| Partitioning Method | Average BLEU | Std Dev |
|---|---|---|
| Random Split | 34.32 | 15.2 |
| Lexical-based | 35.39 | 14.8 |
| Frequency-based | 36.12 | 14.1 |
| Semantic Clustering | 40.14 | 12.3 |
Key Findings:
- Semantic clustering outperforms all baselines by significant margins
- Expert utilization is dramatically higher (89.6% vs ~30% for other methods)
- Lower variance indicates more consistent performance across domains
- Fine-grained specialization enables each expert to focus on coherent semantic concepts
Routing Policy Analysis
| Routing Method | Average BLEU |
|---|---|
| Token-level (Top-1) | 38.74 |
| Token-level (Top-2) | 39.15 |
| Domain-level (Ours) | 40.14 |
| Hybrid (Domain + Token) | 39.87 |
Routing Analysis:
- Domain-level routing achieves highest performance and efficiency
- Semantic coherence at sequence level enables better expert specialization
- Balanced speed without sacrificing accuracy
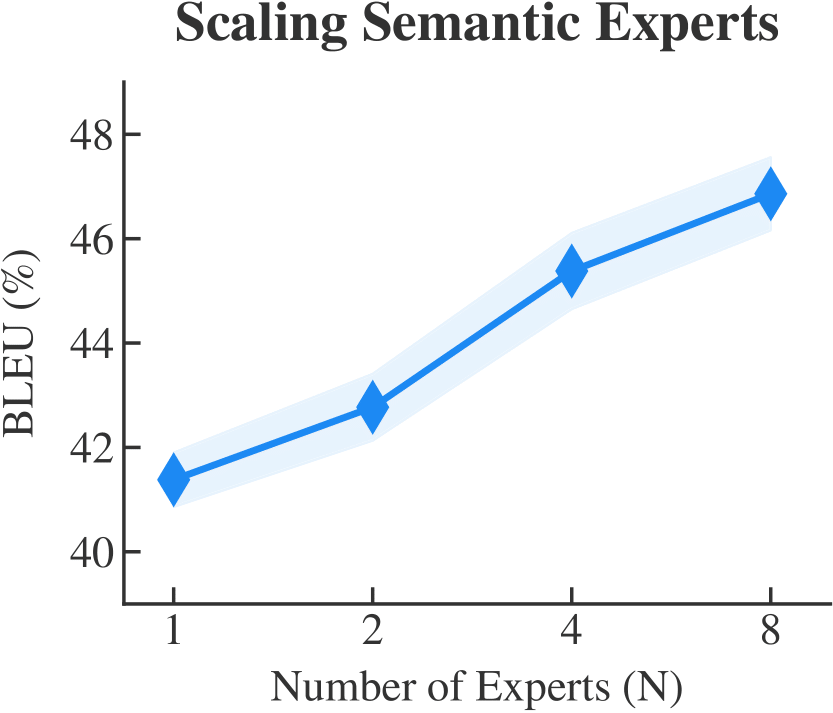
Expert Scaling Analysis
| Number of Experts | WordNet | Oxford | Wikipedia | Urban | 3D-EX | Average | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N=1 (Dense baseline) | 36.99 | 26.09 | 57.90 | 26.09 | 35.01 | 34.63 | - |
| N=2 | 35.42 | 20.15 | 56.78 | 26.33 | 38.91 | 35.52 | +0.89 |
| N=4 | 40.09 | 23.35 | 60.31 | 31.26 | 45.69 | 40.14 | +5.51 |
| N=8 (Optimal) | 42.12 | 24.88 | 61.46 | 33.18 | 47.03 | 41.73 | +7.10 |
Scaling Insights:
- Peak at N=8: Optimal balance between specialization and generalization
- Consistent gains: Performance will increase as the number of expert increases.
- Over-specialization: Too many experts may lead to data sparsity per expert, exhibiting on the slowly growing performance gains.
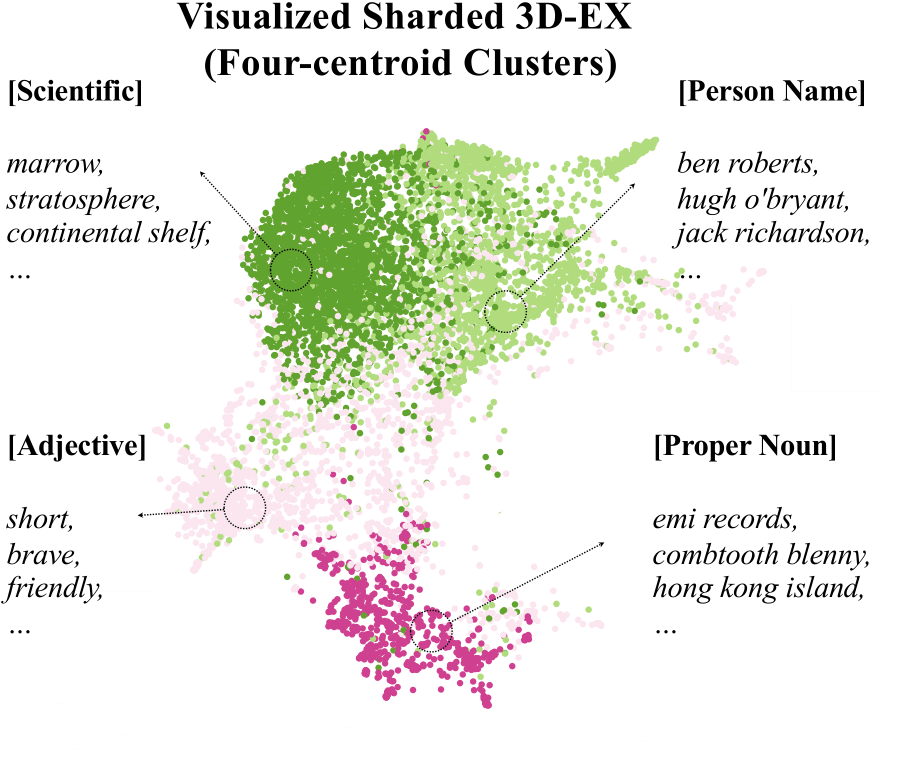
Clustering Quality Analysis
| Cluster ID | Dominant Category | Sample Terms | Intra-cluster Similarity | Expert Performance (BLEU) (%) | Data Distribution (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
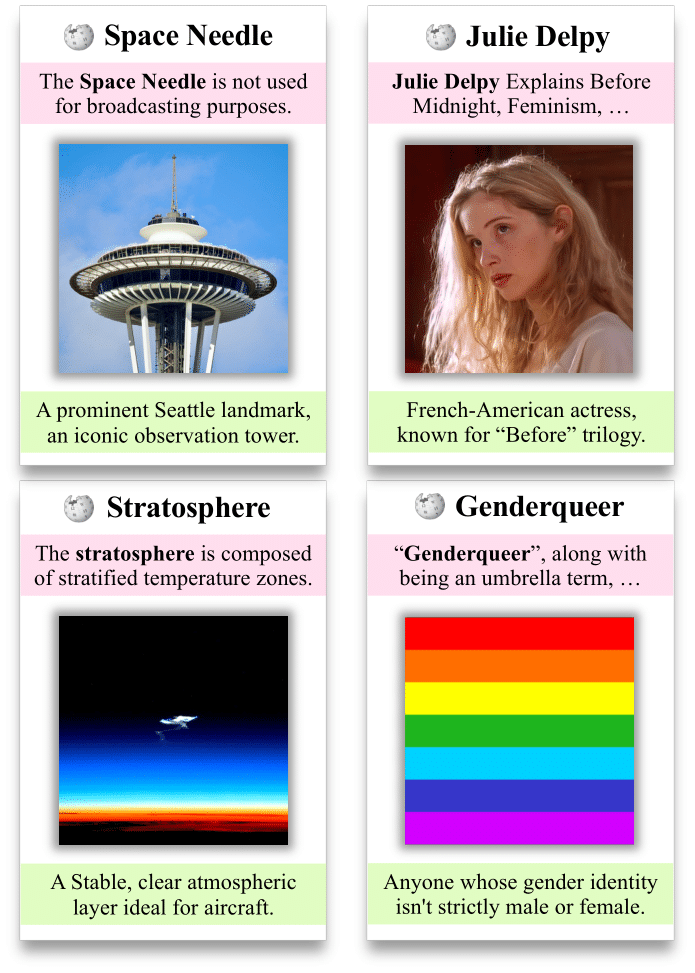
| Cluster 0 | Scientific Terms | stratosphere, photosynthesis, quantum | 0.87 | 42.3 | 28.4% |
| Cluster 1 | Person Names | Julie Delpy, Einstein, Shakespeare | 0.92 | 45.7 | 22.1% |
| Cluster 2 | Social/Cultural Terms | genderqueer, democracy, tradition | 0.83 | 38.9 | 31.8% |
| Cluster 3 | Adjectives/Descriptors | beautiful, complex, efficient | 0.79 | 35.2 | 17.7% |
Analysis of semantic clusters showing clear specialization patterns. Higher intra-cluster similarity correlates with better expert performance.
LM-Lexicon Pipeline Visualization
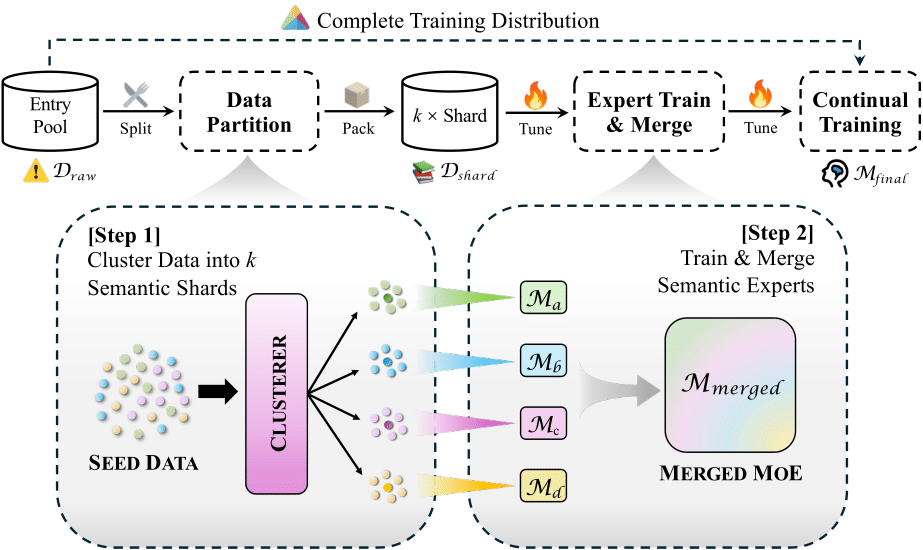
Training Pipeline Overview: The three-stage training recipe showing data clustering, expert training, and model merging phases of LM-Lexicon.